Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Explained
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is one of the fastest-growing trends in business automation. It allows organizations to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks using software “robots” that mimic human interactions with digital systems.
Consider RPA as digital workers that perform routine tasks across different applications — allowing human staff to concentrate on more strategic work. Rather than having people click through screens, transfer data, or generate reports manually, RPA bots can execute these operations automatically — enhancing efficiency, precision, and adaptability.
Unlocking the Power of RPA: What You Need to Know
RPA is a technology that enables bots to interact with applications and systems just like a human would:
- Clicking buttons
- Entering or copying data
- Navigating menus
- Sending emails or notifications
Unlike traditional automation (which requires deep system integration), RPA works on top of existing systems — often without changing the underlying applications.
Typical Use Cases
RPA shines in high-volume, repetitive, rules-driven tasks, for example:
- Finance & Accounting → invoice processing, expense report handling
- HR → employee onboarding, payroll, benefits administration
- IT Services → automated password resets, system monitoring
- Customer Service → data entry, order status checks
- Compliance → audit trail creation, regulatory reporting
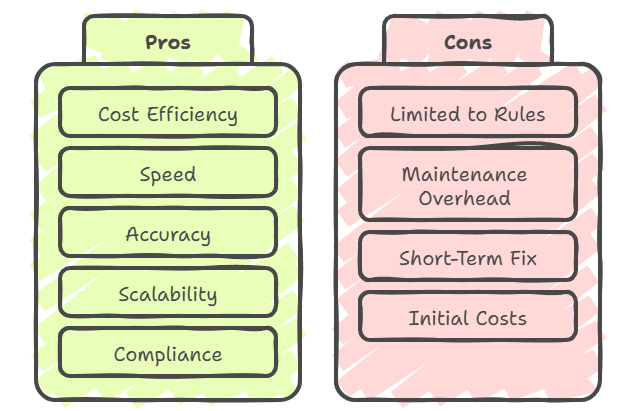
RPA: Game-Changing Benefits & Key Challenges to Consider
Future of RPA
RPA is increasingly part of Hyperautomation, where it works alongside:
- BPM (Business Process Management) for orchestration
- AI/ML for intelligent decision-making
- Process Mining to identify automation opportunities
RPA vs. Intelligent Automation
Classic RPA is rule-based. The next evolution is Intelligent Automation (IA), which combines RPA with AI/ML:
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition): Extracting data from PDFs and scanned documents
- NLP (Natural Language Processing): Understanding text from emails or chats
- ML Models: Making decisions based on data patterns
This combination extends RPA beyond simple rule execution into cognitive automation.
- UiPath – Leader in enterprise RPA platforms
- Automation Anywhere – Cloud-native RPA with AI integrations
- Blue Prism – Enterprise-grade automation for large organizations
- Microsoft Power Automate – Low-code automation with Office 365 integration
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation enables organizations to save time, cut costs, and improve accuracy by automating repetitive tasks.
For anyone working in automation, RPA skills are an essential foundation — and a stepping stone towards the future of Hyperautomation.
![[PROJECT] Smart Inbox Automation with n8n — Auto-categorize Emails and Trigger Custom Actions](/assets/images/PRJ-n8n/cover-n8n.png)

Comments